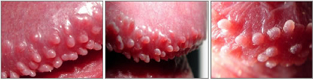
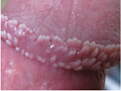
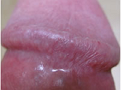
Pearly Penile Papules (PPP)
PPP, officially known as Hirsuties papillaris genitals, are small fleshy bumps that form at the corona of a penis. They are given such name because they often appear in small rows like strings of pearls.
PPP is not a disease though this condition is very common and affects approximately 25% of men worldwide. Some studies showed that they are more common in uncircumcised men. However, you have absolutely nothing to worry about since they do not cause any pain, itching or burning. They cannot be spread through sexual contact.