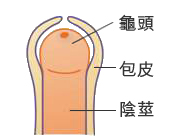
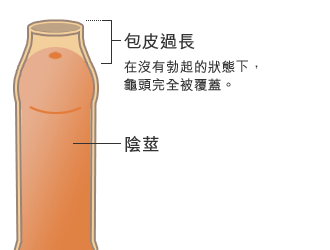
Traditional Circumcision
The excessive foreskins can be surgically removed to enable the exposure of glans. Surgeries, which take roughly 30 to 45 minutes, can be done in outpatient settings with local anesthesia. After surgeries, wounds are sewn up using dissolvable stitches. Patients can return to most normal activities immediately following the surgeries and urination will not be affected. Painkillers can be taken to alleviate discomfort or pain. The stitches will disappear in 7 to 10 days and patients can resume sexual activities after 3 to 4 weeks.
Laser Circumcision
Excessive foreskins can be removed by using a laser beam. This method prevents excessive bleeding since only small wounds are created. It also allows exact proportions of skin and mucous membrane to be removed. After the application of local anesthesia, it takes roughly 20 minutes to complete the surgery. Patients do not have to clean their wounds in a week’s time following the surgeries and full recovery is expected in 3 to 4 days. Less pain will be caused when compared with the traditional method and hence, fewer painkillers are needed.
New Laser Circumcision
A specialized metal ring is used in the new version of laser circumcision (patent application for this treatment has been filed). This would give better protection to patients and would avoid removing too much or too less skin. The ring is to be put around the penis shaft and then be covered by the excessive foreskin which is going to be removed. The ring helps protect the penis during the surgery. An adjustable loop will then be placed at the concave side of the ring to fix the excessive skin area that is going to be removed. Bleeding would then be reduced.
Compared with the old laser circumcision, this improved version gives better protection to the penis and also allows more precise laser removal of the foreskin, avoiding the removal of excessive skin which often happens in traditional circumcision.
Furthermore, this new laser circumcision would only require patients to receive one shot of local anesthetic at the bottom of the penis shaft, instead of three in the old laser and traditional circumcision (two at the back of the penis shaft and one at the bottom). After the application of local anesthetic, it would take around 15 to 20 minutes to complete the surgery. Wound cleaning is not required after surgery. It will be completely recovered after three to four days. Only mild pain occurs; it is not required to take high dose of pain-killer.
Comparison between Traditional and Laser Circumcision
| |
New Laser
Circumcision |
Old Laser
Circumcision |
Traditional
Circumcision |
| Principles of surgery |
A specialized metal ring is put around the penis shaft and then be covered by the excessive foreskin which is going to be removed. An adjustable loop will be placed at the concave side of the ring to fix the excessive skin area that is going to be removed. Bleeding would then be reduced. |
Excessive foreskins can be quickly removed by using a laser beam. Excessive bleeding can be prevented since only small wounds are created. |
The excessive foreskins can be surgically removed to enable the exposure of glans |
| Anesthesia methods |
one shot of local anesthetic at the bottom of the penis shaft |
Three shots of local anesthetic are applied, two in the back of the penis shaft and one in the bottom. |
Three shots of local anesthetic are applied, two in the back of the penis shaft and one in the bottom. |
| Surgical time |
15-20 minutes |
15-20 minutes |
30 minutes |
| Bathing |
Next day after surgery |
Next day after surgery |
2-3 days after surgery |
| School or Work |
1-2 days after surgery |
1-2 days after surgery |
4-5 days after surgery |
| Exercises |
2 weeks |
2 weeks |
4 weeks |
| Sexual activity |
4 weeks |
4 weeks |
6 weeks |
| Bleeding |
Minimal bleeding |
Minimal bleeding |
Higher risk of bleeding |
| Postoperative pain |
Mild |
Mild |
Moderate to severe |